As an infinitely recyclable material, copper is well-known for its strong sustainability credentials.
Not only is the red metal supporting the shift to a circular economy, but it’s also helping to accelerate the transition to renewable energy.
A key component of electrical wiring, copper plays an important role in the capture, storage and transmission of renewable energy.
Demand for copper is already on the rise and will continue to grow as the green energy transition gathers pace.
The rising demand for copper
Global refined copper usage has risen steadily over recent decades, and in the last few years, the rate of growth has hit new heights.
While usage in non-energy markets like plumbing and construction has increased, most of the growth can be attributed to rises in demand for electrical copper wiring.
Current forecasts for global refined copper demand sit at around 25.5 million tons for 2023. To meet net-zero emissions by 2050, global copper supplies will need to rise by nearly double within the next 15 years.
Work is underway within the copper industry to rapidly scale supply through increases in primary production and further development of copper recycling infrastructure.
Why is copper used for electrical wiring?
Durable, ductile and highly conductive, copper is well suited to electrical wiring and has been described by experts as “the metal of electrification”.
The red metal is second only to silver in terms of electrical conductivity – and much more abundant – making it the material of choice for storing and transporting electricity.
Compared to other conductors, copper has a high density of free electrons, which means electricity can pass through the metal efficiently.
Not only that, but electrical copper wires bend easily without breaking and can also be recycled repeatedly.
Learn more about copper’s impressive properties below.
How is copper used in renewable energy systems?
Copper is used as a conductor in a wide range of renewable energy systems, including wind turbines, solar panels and electric vehicles (EVs).
In fact, renewable energy systems contain around five times as much copper compared to traditional power generation systems.
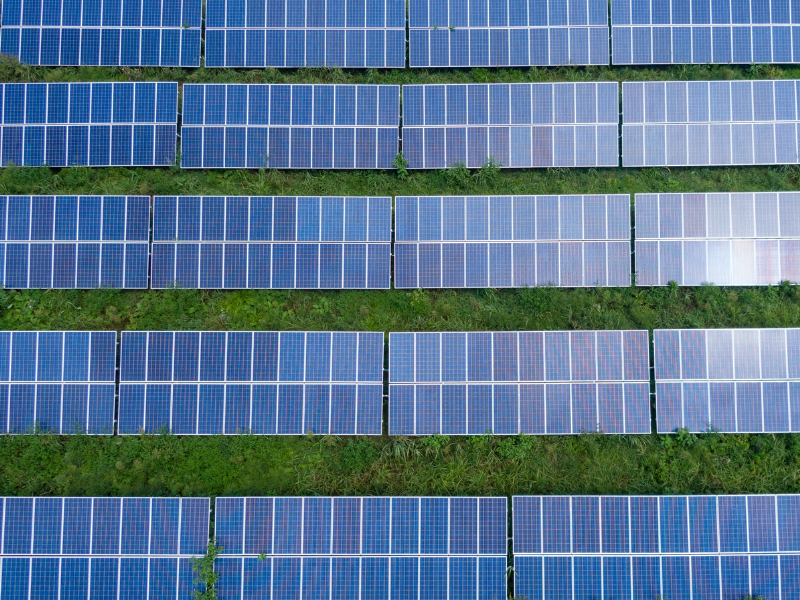
Solar panels
Not only is copper a great conductor of electricity, but it is also considered one of the best metals for conducting heat.
The material has long been used in central heating systems, where copper pipes transfer heat from a boiler to radiators within a building.
This same ability to transfer heat efficiently is now finding use in solar panels.
Copper is a key component of the heat exchangers used in solar panels and the grid lines that connect them to substations, helping to capture and transport solar energy.
Electrical copper wiring is also used to make the cables that transmit the electricity captured in the solar cells.
Overall, it’s estimated that a solar power plant uses 2,450–6,985kg of copper per megawatt of power generation.


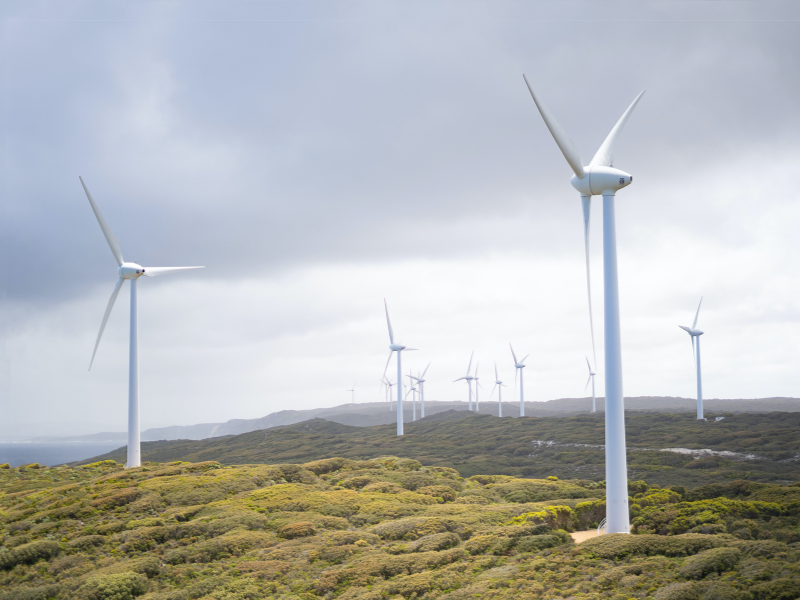
Wind turbines
Copper is equally important in the generation of wind energy, with a typical 660-kW turbine containing around 350kg of copper.
Within the generator, copper is used in the coils of the stator and rotor, helping to convert the mechanical energy captured by the wind into electrical energy.
Copper coils can also be found in the windings of transformers, the parts responsible for changing the voltage of the energy and transporting it to the load.
As with solar panels, vast networks of copper wires are used to transmit and distribute energy from on-shore and off-shore wind farms to local grids.
Offshore wind farms are known to use even more copper than onshore plants due to the additional cabling needed to transport energy to the substation.

Electric vehicles
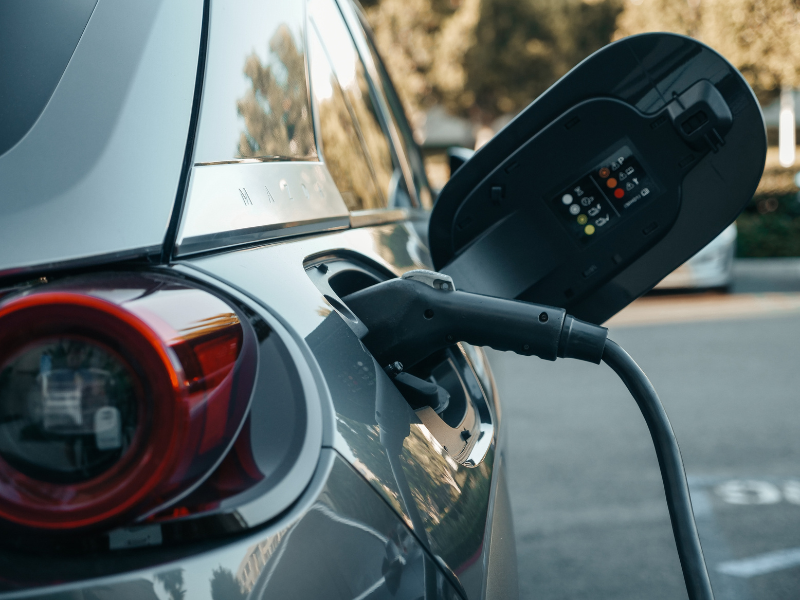
Most of the demand for copper in the energy transition comes from electric vehicles (EVs), with the red metal used in batteries, motors, wiring systems and charging infrastructure.
In the EV’s powertrain, high-performance copper cables support rapid energy transfer from the battery to the motor.
Electrical copper wires are also used widely in charging units, with the material’s excellent conductivity allowing for efficient charging.
Fully electric vehicles can use as much as 80kg of copper, which is up to four times the amount used in an internal combustion engine vehicle.


Copper: a critical material for the future
Copper has been key to human progress for thousands of years, and the material promises to continue driving innovation through the energy transition.
Want to learn more about how copper is shaping a more sustainable future? Check out our other news items or sign up for our newsletter.